March 20th, 2025
Category: business intelligence,Manufacturing
No Comments
Posted by: Team TA

What is Business Intelligence in Manufacturing?
Business intelligence (BI) in manufacturing is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from manufacturing operations to improve decision-making. It collects data from machines, supply chains, and quality control, enabling companies to optimize operations, improve product quality, and reduce waste.
A business intelligence platform combines data from many sources into user-friendly dashboards, enabling stakeholders to monitor important performance indicators in real-time. This enables manufacturers to improve supply chain management, forecast demand accurately, and adapt quickly to market changes for sustained growth.
Key Features of BI in Manufacturing
- Data Collection: Pulling information from various sources like machines, sensors, ERP systems, and customer feedback.
- Data Integration: Combining data from different sources into a central location for easier analysis.
- Visual Reporting: Using charts and graphs on dashboards to quickly understand key metrics and trends.
- User-Friendly Data Access: Empowering staff to access, modify, and store data without requiring IT support.
- Predictive Analytics: Using data science and AI for forecasting and predictive modeling.
- Secure Access Control: Protects data with role-based permissions and activity tracking.
The industry is undergoing a data-driven transformation, where companies are using analytics to enhance productivity, customer experience, and sustainability. However, just 39% of manufacturing executives surveyed by the Boston Consulting Group in 2021 had successfully scaled data-driven applications beyond single-product production to produce favorable business outcomes. This emphasizes how manufacturing needs to use data more effectively.
As the manufacturing sector generates massive volumes of data across production, supply chains, and sales, the importance of business intelligence (BI) software is increasing. Manufacturers are turning to BI tools to unlock the valuable insights hidden within this data.
Manufacturing plays an important role in the global economy, with an output projected to reach US$49.3 trillion by 2025, according to Statista.
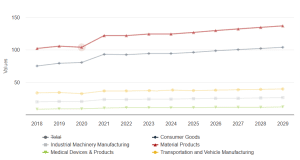
Source: Statista
This article will explore why manufacturers need BI tools, the essential features of such tools, and how they are commonly applied within the industry, aiming to provide a clear understanding of BI’s role in modern manufacturing.
How Business Intelligence Improves Your Manufacturing Processes?
1. Transforming Data into Insights
Business intelligence (BI) transforms raw manufacturing data into actionable insights through intuitive dashboards. By combining data from multiple sources, these dashboards offer a concise summary of trends and key performance indicators (KPIs). Real-time data visualization gives stakeholders the ability to optimize procedures and make well-informed adjustments.
BI dashboards that are customized to meet the demands of company and user needs. Manufacturers leverage BI to monitor the entire supply chain, from production to delivery, ensuring targets are met. BI tools also improve inventory planning and demand forecasting, which boosts productivity and gives businesses a competitive edge.
2. Driving Production Management
By reducing machine downtime and streamlining operations, business intelligence (BI) greatly enhances production management. BI software can forecast equipment breakdowns by utilizing machine learning, facilitating preventative maintenance, and preventing expensive disruptions. Integrating IoT further enhances predictive accuracy through real-time data collection from connected devices.
By gathering input from stakeholders and customers, BI also aids in product development, leading to better features and designs. Furthermore, BI analytics tracks key performance indicators like downtime and defect rates. Manufacturing companies can use this approach to identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and increase efficiency and productivity.
3. Improving Inventory Control
By providing insights into stock levels and turnover rates, business intelligence (BI) optimizes inventory control. Manufacturers can prevent overstocking and stockouts by optimizing stock management with predictive analytics and product fault monitoring.
BI also enhances demand forecasting by combining internal and external data. This leads to more accurate production planning and order fulfillment. Reducing inventory management labor, also minimizes the risk of stockouts, thereby boosting profitability.
4. Enhancing Supply Chain Monitoring
BI provides manufacturers with real-time supply chain visibility, tracking key performance indicators and ensuring timely deliveries. This strengthens supplier relationships and improves overall efficiency by minimizing disruptions.
By analyzing data from partners, Business Intelligence (BI) helps monitor inventory levels, lead times, and costs effectively. This allows manufacturers to proactively identify risks, streamline operations, and adapt to market changes for smooth production workflows.
5. Streamlining Workforce Operations
Business intelligence (BI) streamlines workforce operations by optimizing resource allocation. Using data analysis, manufacturers can ensure that the right number of employees are available for different hours and tasks.
Additionally, BI tools track performance indicators like safety and productivity, enabling targeted training initiatives to improve staff skills. This data-driven strategy promotes better decision-making at all levels of the organization and cultivates a talented workforce.
6. Improving Finance Management
By offering precise data for forecasting, cost optimization, and budgeting, BI improves financial management in the manufacturing sector. By analyzing financial figures across production, operations, and sales, BI helps manufacturers create well-informed budgets and pin-pointing areas where costs can be cut without compromising productivity.
Additionally, BI conducts comprehensive financial studies, including cost-benefit analyses and profit and loss assessments. By using sophisticated forecasting technologies, manufacturers can ensure long-term growth and profitability.
7. Reducing Costs and Improving Profitability
Manufacturers can make better financial decisions and increase profitability by using BI to find hidden inefficiencies and their cost triggers. Understanding product costs and margins through unit economics analysis allows for optimal pricing.
By increasing visibility into purchase orders and supply chain costs, BI improves cost management. Stronger supplier agreements, more efficient inventory, and improved cash flow management are all made possible by accurate data, which lowers expenses and increases profitability.
Real-life Examples of BI in Manufacturing

- General Electric (GE)
General Electric (GE) uses business intelligence (BI) to increase efficiency and drive growth by analyzing real-time data from its manufacturing operations. The company has integrated BI with advanced machine learning so that it can recognize patterns, prevent equipment failures, and conserve energy. Such a proactive approach reduces downtimes, minimizes maintenance costs, and drives higher productivity.
- Boeing
Boeing, a global leader in aerospace, has leveraged business intelligence to manage its complicated manufacturing and supply chain operations. By collecting and analyzing data from production lines, suppliers, and maintenance systems, they can monitor real-time production status and quality metrics.
Boeing can forecast demand for airplane components and spare parts using predictive analytics thanks to BI. This guarantees timely deliveries and optimal inventory levels, illustrating how data-driven decision-making improves operations and customer satisfaction in practical applications.
- Toyota
Toyota, known for its Toyota Production System (TPS), uses business intelligence (BI) to enhance efficiency and quality. By analyzing data from production lines, supply chains, and customer feedback, Toyota tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) like cycle times, inventory levels, and defect rates. This helps identify areas for improvement and drive continuous process enhancements.
Additionally, Toyota leverages BI for demand forecasting, optimizing production schedules, and inventory management. This ensures timely vehicle deliveries while reducing waste and costs, demonstrating how data-driven insights support efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
The role of business intelligence (BI) in manufacturing is expanding rapidly, driven by AI and advanced analytics. According to ABI Research, industrial enterprises are expected to generate 4.4 Zettabytes (ZB) of data by 2030, up from 1.9 Petabytes in 2023. This surge highlights the growing need for BI to manage and analyze massive data volumes effectively.
BI in the manufacturing industry will continue to be essential for streamlining supply chains, productivity, and decision-making as industries adopt digital transformation. Choosing suitable BI tools will boost productivity, creativity, and competitiveness, guaranteeing that companies maintain their lead in the rapidly changing global economy.
Travancore Analytics leads in business intelligence, providing essential tools for manufacturers to enhance performance and efficiency. We offer BI development services to help you gain valuable insights and optimize operations.